Obesity is one of the major risks for development of Type 2-Diabetes.
WHY OBESITY IS A RISK FACTOR FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES?
An increase in body mass leads to beta cells dysfunction and eventually failure.
On the other hand, weight loss can reduce the risk of diabetes.
According to world obesity atlas March 2023, adult obesity in India will grow at a annual rate of 5.2% and obesity in children by 9.1% by 2035.
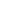
Weight can be categorized using the body mass index measurement.

Weight categories and risk factor of Diabetes
BMI is an independent and strong risk factor for type 2-diabetes.
In obese person, the amount of free fatty acids, glycerol, hormones, cytokines and other substance which are involved in development of insulin resistance is increased.
As the BMI increases, there is a concurrent increase in the risk of type 2 diabetes.
some researchers believe that people with obesity who have no other health problems are still at increased risk for developing obesity-linked conditions, such as metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease in the long term.
Let us now discuss the risk of diabetes based on the BMI.
- An individual with BMI less than 18.5 is considered underweight.
- A healthy individual will have a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- An individual with a BMI of 25 to 29.9 is considered overweight.
- An individual with BMI greater than 30 is categorized as obese.
Waist Measurement and obesity
The waist circumference is associated with central obesity and insulin resistance.
To measure the waist an individual should,
- Place a tape measure around the bare abdomen halfway between the bottom of lowest rib and the top of hip bones
- Make sure the tape is snug but is not digging into the skin and is parallel to the floor
- Relax, exhale and measure
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3178283/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24694251/
https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/index.html
www.idf.org