Diabetes is group of metabolic disorders characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from not producing any or enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin that is produced.
When we eat food, it is digested in the digestive tract. Most of the food we eat is broken down into glucose.
Glucose is a form of sugar in the blood, which is carried by the blood to all the cells throughout the body.
It is the principal source of fuel for our body which gives energy and helps us grow.
In the body an organ called pancreas, makes a hormone (chemical) called Insulin, which helps glucose (sugar) move from the blood into the cells.
Insulin helps the cells get the glucose (sugar) needed for energy.
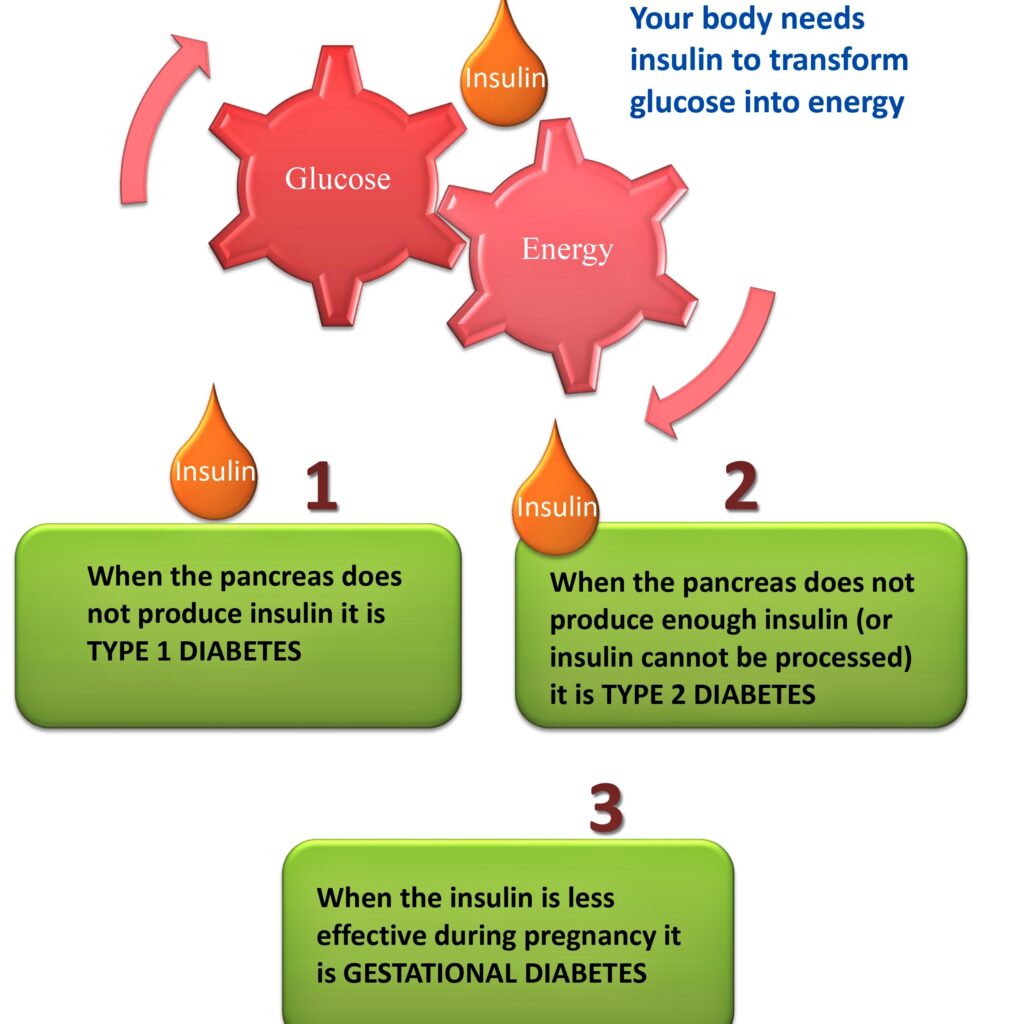
Your body needs insulin to transform glucose into energy
Insulin also helps keep the blood sugar levels normal.
If someone is diabetic, the pancreas makes little insulin or no insulin, or the cells cannot use that insulin very well.
Glucose (sugar) cannot get into cells and builds up in the blood, resulting in high blood glucose levels.
If the blood glucose stays too high, it can damage many parts of the body such as the heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, blood vessels, etc.
Diabetes is one of the largest and fastest growing global healthcare emergencies of the 21st century.
What are the types of Diabetes?
We shall now discuss the different types of diabetes.
The most accepted and conventional classification of diabetes is
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)
- Gestational Diabetes
- Other types of Diabetes

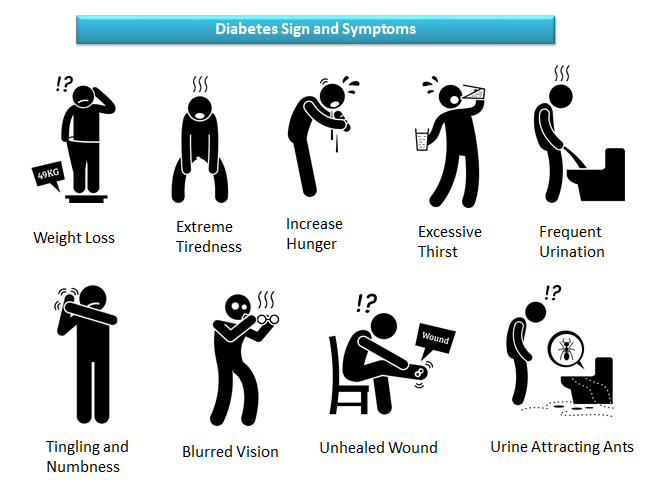
What Are The Sign & Symptoms Of Diabetes?
- Weight loss
- Extreme tiredness
- Increased Hunger (Polyphagia)
- Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia)
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
- Tingling and numbness
- Blurred vision
- Unhealed wound
- Urine attracting ants.
What is difference between Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes?
Comparison between a healthy individual and those with Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes
Healthy Person :
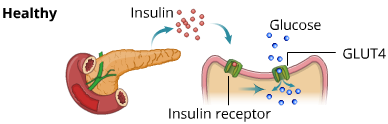
In a healthy individual, insulin secreted by the pancreas attaches to the insulin receptor and permits the entry of glucose into the cells, thereby maintaining the blood glucose levels
Type 1 Diabetes Person:

In individuals with Type 1 diabetes or T1DM, the pancreas fails to secrete insulin due to the development of autoantibodies that destroy the islet cells, the cells that produce insulin or the enzymes involved in the process of insulin secretion. Therefore, these individuals have absolute deficiency of insulin, which leads to high blood glucose levels
Type 2 Diabetes Person:
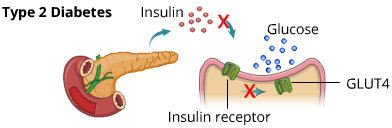
In individuals with Type 2 diabetes or T2DM, there is a problem between coupling of insulin with its receptors (insulin resistance) or the amount of insulin is insufficient (secretory deficiency) resulting in impaired movement of glucose from extracellular to intracellular space, causing an increase in the blood glucose level.
What are the range of blood sugar levels of Diabetes?
Knowing the recommended levels for your blood sugar can help you figure out if its in normal range or not.
your doctor will tell you to do some blood tests to make sure of the diagnosis and also the right range of blood sugars for you based on your health and medical history.
Test for Type 1 Diabetes,Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes:
Fasting Blood Sugar Test Or FPG (Fasting Plasma Glucose Test):
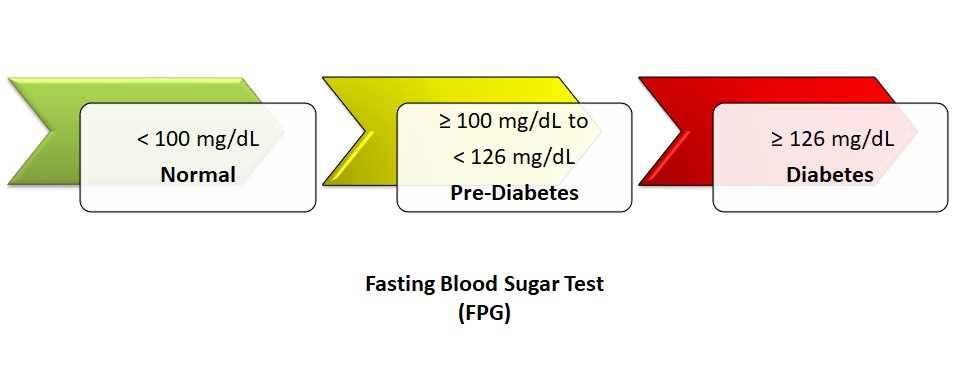
This test checks your blood sugar after not eating overnight. If your fasting blood sugar is 99 mg/dL or lower, its normal. A level of 100 to 125 mg/dL means you have prediabetes, and 126 mg/dL or higher means you have diabetes.
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Test:
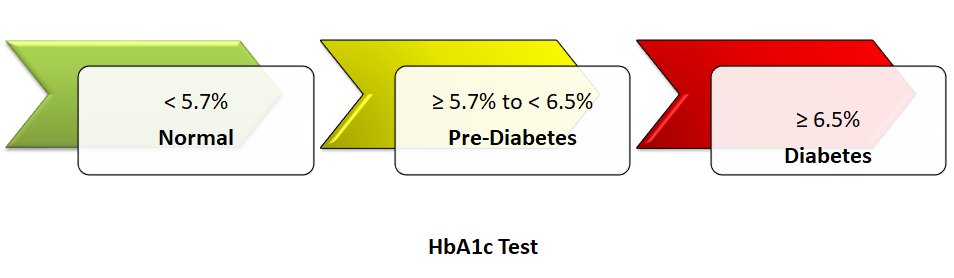
The HbA1c test shows your average blood sugar level for the past 2 or 3 months. If your HbA1c is below 5.7%, Its normal. If its between 5.7% and 6.4%, It means you have Prediabetes. HbA1c of 6.5% or higher indicates you have diabetes.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test or Glucose Tolerance Test:
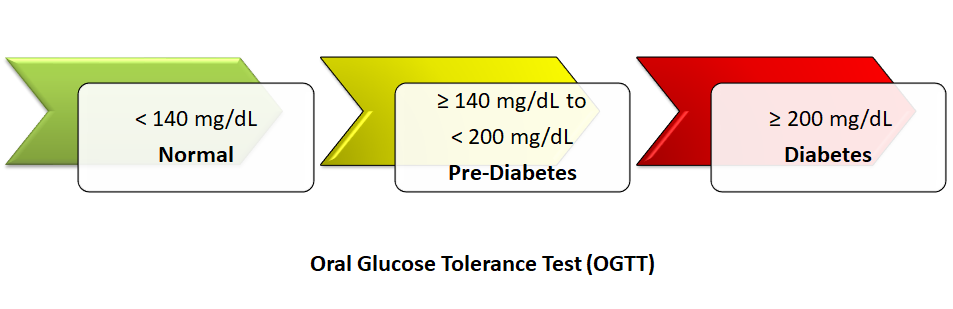
This test checks your blood sugar before and after drinking a glucose containing liquid. You will need to not eat overnight before the test, and they will draw blood to check your fasting blood sugar level. After drinking the liquid, they will check your blood sugar after 1 hour, 2 hours, and maybe 3 hours. If your blood sugar is 140 mg/dL or lower at 2 hours, its normal. between 140 to 199 mg/dL means you have prediabetes, and 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
Random Blood Sugar Test:
This test checks your blood sugar right when you are tested. you can take this test any time without fasting (not eating) first. If your blood sugar is 200mg/dL or higher, It means you have diabetes.
If your doctor suspects you have type 1 diabetes, they might check your blood for substances called autoantibodies, which show that your body is attacking itself. These are usually found in type 1 diabetes and not in type 2 diabetes. They may also test your urine for ketones, which are produced when your body burns fat for energy. Finding ketones in the urine can suggest type 1 diabetes instead of type 2 diabetes.
What are the Myths About Diabetes ?
TRUE OR FALSE
EATING TOO MUCH SUGAR CAUSES DIABETES
FALSE : when kids get type 1 diabetes, it’s because their bodies can’t make insulin anymore. It has nothing to do with eating too much sugar. When kids get type 2-diabetes there might be a connection because eating too much sugar (or foods with sugar, like toffees or soft drinks) can cause weight gain and weight gain can lead to type 2-diabetes.
TRUE OR FALSE
PEOPLE WITH DIABETES SHOULD NOT EXERCISE
FALSE: Exercise is important for all people- with or without diabetes. Exercise has many benefits. It keeps people healthy and fit. And also helps them balance their blood sugar.
TRUE OR FALSE
YOU CAN CATCH DIABETES FROM ANOTHER PERSON
FALSE: Diabetes is not contagious, so you can’t catch it from someone who has it.
TRUE OR FALSE
PEOPLE WITH DIABETES CAN NEVER EAT SWEETS
FALSE: People with diabetes can eat sweets- as part of a balanced, healthy diet. Like everyone else, a person with diabetes should not eat too many sweets because they may cause damage to teeth and they don’t have many vitamins and minerals.
References:
IDF diabetes Atlas 10th edition, Accessed Jan 3,2024
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/diabetes.html Accessed Jan 3,2024
