- Type 1 diabetes or T1DM is diagnosed when the pancreas stops making insulin completely.
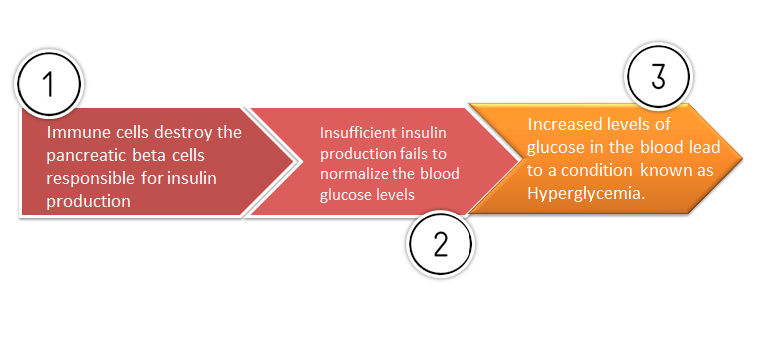
- It is an autoimmune disease which means the body’s own immune system attacks the pancreas destroying the cells that make insulin. This results in the body being unable to control the amount of sugar in the blood.
- Its previously also called as insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes
- Diabetes can develop in a child of any age, including infants and toddlers. Diabetes can affect both boys and girls.
- Type 1 diabetes often develops quickly and maybe life-threatening if not diagnosed early.
- Generally presents in children and young adults.
- Person has to take insulin through injections or the external sources such as insulin pumps to control their blood sugar.
- Despite major advances, T1DM is not preventable.
What are the risk factors of Type 1 Diabetes?
Evidence suggests that individuals with,
- Family history of diabetes: Individuals with a parent or sibling with Type 1 diabetes are more likely to develop type1diabetes.
- Genetics: Presence of certain Genes.
- Geography: Higher incidence in people living in regions away from the equator.
- Exposure to certain viral infections: Exposure to Epstien-Barr virus, Coxsackie virus, Mumps virus & Cytomegalo virus
- Environmental Factors: Early exposure to Cow’s Milk.
As a Person, What do I need to know about Type 1 Diabetes?
Children with type 1 diabetes,
- Should eat their meals at an appropriate time and have enough time to finish the meal.
- Need to do blood sugar checks regularly
- Should have free and unrestricted access to water and the bathroom
- May need to eat snacks outside scheduled mealtimes.
- Need to inject insulin in a safe place and at prescribed times
- Sometimes can have low sugar levels in blood called hypoglycemia which needs to be managed
- Can participate fully in physical education and other extracurricular activities (including field trips, camps, picnic, etc.)
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosed ?
For the diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes, the presence of one or more auto immune markers are tested such as :
- Islet cell autoantibodies
- Autoantibodies to insulin
- Autoantibodies to GAD (GAD65) GAD: glutamic acid decarboxylase
- Autoantibodies to the tyrosine phosphatases IA-2 and IA-2β (IA=Islet Antigen)
- Autoantibodies to zinc transporter 8 (ZnT8).
- The first-degree relatives of a person with T1DM can also be offered screening for diabetes.
- For screening of diabetes and pre-diabetes, the same tests are used as for the diagnosis.
- Early diagnosis is the key to better clinical outcome
References:
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/what-is-type-1-diabetes.html Accessed: Jan 8,2024
Idf diabetes atlas. 2021. Accessed: Jan8,2024
