- Formerly known as ‘Non-insulin-dependent’ or ‘Adult – onset diabetes.
- It is most predominant type of diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes usually develops in individuals after the age of 45 years, but can also occur in younger adults & children.
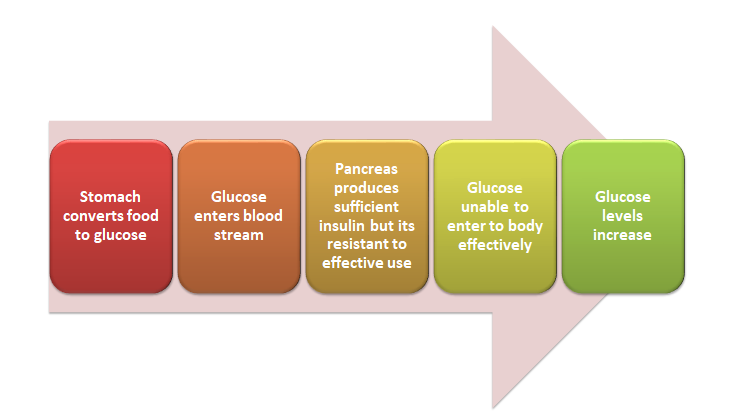
- Although the body is able to produce insulin, inability of the cells to use insulin efficiently due to insulin resistance.
- Progressively the amount of insulin produced also declines gradually.
- As a result, insulin fails to adequately mobilize glucose from blood to the organs such as liver, fat and muscle cells leading to high blood sugar levels or hyperglycemia.
What are the risk factors of Type 2 Diabetes?
The risk factors for Type 2 Diabetes include,
- Family history of diabetes:
Parents or sibling with type 2 diabetes. - Genetics:
Presence of certain genes - Ethnicity: African Americans, Asian Americans, Latino/Hispanic Americans, Native Americans or Pacific Islanders are at higher risk.
- History of gestational diabetes
- Obesity
- High blood pressure.
- Abnormal lipid levels
- Unhealthy eating habits.
- Poor nutrition.
- Physical Inactivity
- Increasing age
- Hypertension
- Intermediate Hyperglycemia (Pre-Diabetes).
Why do people need to prevent & take care of type 2 Diabetes?
Because it progresses with age and increasing insulin resistance, leading to the development of micro vascular (Heart related) and macro vascular complications of diabetes such as,
- Damage to the retina
- Kidney disease and more than 70% of patients who suffer from kidney disease have a history of diabetes.
- Foot problems
As Individual, What do I need to know about Type 2 Diabetes?
A person with Type 2 diabetes,
- May need to monitor blood sugar regularly
- Needs to eat healthy food
- Needs to practice physical activity regularly
- Might take insulin or other medications
- Should have free and unrestricted access to water and the bathroom
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed?
| Screening | Diagnosis |
| Consider screening all individuals above the age of 45 years | FBG (fasting blood glucose) can be used for initial diagnosis. |
| Screen overweight & obese teens & adults and those with abnormal obesity | FBG > 126 mg/dL or 7.0 mmol/L is diagnostic |
| Measure the BMI and waist circumference to identity overweight and obese individuals | Confirm the diagnosis with HbA1c measurement, HbA1c = Glycated Haemoglobin |
| Asians with a BMI of > 23 kg/m2 need screening for diabetes | HbA1c > 6.5% is diagnostic |
| Screen those individuals with parents or siblings with T2DM | Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) can be used for screening and diagnosis for T2DM and gestational diabetes |
| Screen mothers with gestational diabetes in the past pregnancy |
References:
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html Accessed: Jan10,2024
https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565257 Accessed: Jan10,2024
Idf diabetes atlas 2021 Accessed: Jan11,2024
